what is Scrum? | A Comprehensive Guide
What Is Scrum?
In the realm of project management, understanding "What Is Scrum" has become increasingly vital, especially in Agile environments. Embraced for its flexibility, adaptability, and collaborative nature, Scrum has revolutionized the way teams approach complex projects. Let's delve into what Scrum truly entails and how it operates within the broader context of Agile methodology.
Core Elements of Scrum:
Scrum Roles:
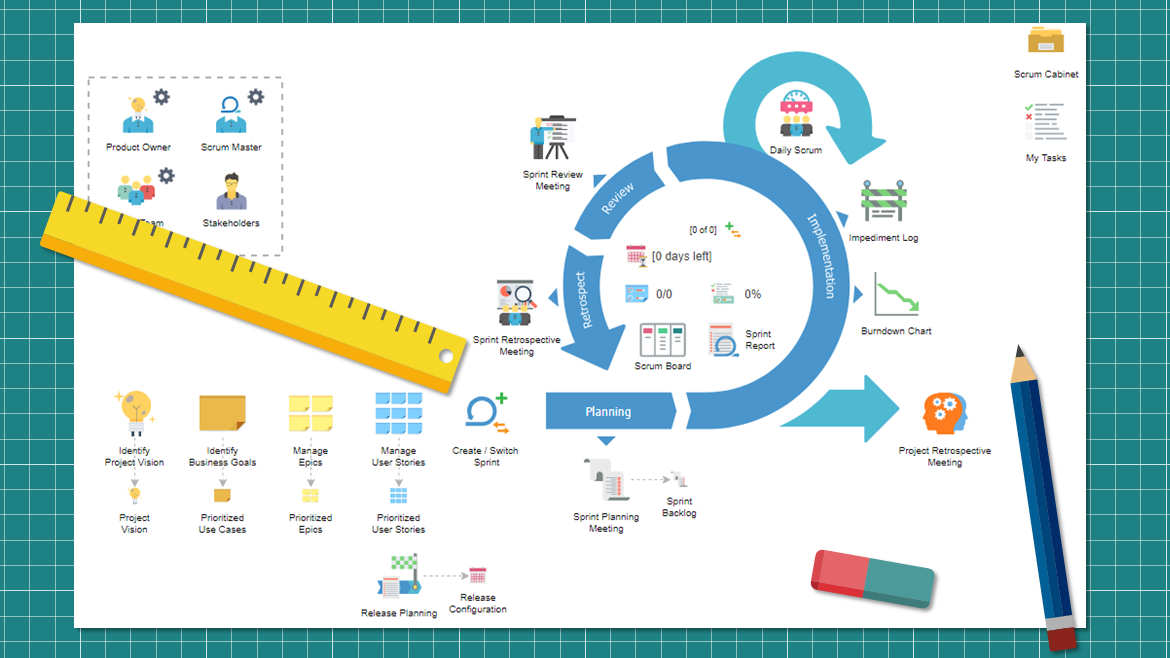
Scrum defines three primary roles: Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team.
Scrum Events:
Scrum events, also known as ceremonies, include Sprint Planning, Daily Stand-ups, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective.
Scrum Artifacts:
The three key artifacts in Scrum are the Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Increment.
Scrum Roles: Scrum defines three primary roles: Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team.
Scrum Events: Scrum events, also known as ceremonies, include Sprint Planning, Daily Stand-ups, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective.
Scrum Artifacts: The three key artifacts in Scrum are the Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Increment.
How Does Scrum Work?
At the heart of Scrum lies the concept of "Sprints," time-boxed iterations during which the team creates potentially shippable increments of the product.
Benefits of Scrum
The adoption of Scrum offers several advantages to organizations and project teams:
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Scrum's iterative nature allows for quick adjustments based on changing requirements or feedback, ensuring the delivered product remains aligned with stakeholders' needs.
- Enhanced Communication and Collaboration: The framework promotes regular interaction among team members, fostering better communication, knowledge sharing, and a cohesive working environment.
- Increased Transparency: With the use of visual tools like burndown charts and task boards, Scrum provides transparency into project progress, enabling better decision-making and risk management.
- Faster Time-to-Market: By delivering increments of the product at the end of each sprint, Scrum accelerates the delivery process, enabling faster time-to-market and quicker response to market demands.
Challenges and Considerations
While Scrum offers numerous benefits, its implementation may face challenges such as resistance to change, difficulties in estimating work accurately, and the need for a robust understanding of the framework by all team members. Additionally, for organizations transitioning from traditional methodologies to Scrum, cultural and structural shifts might be required to embrace its principles fully.
Conclusion
Scrum, with its emphasis on adaptability, collaboration, and iterative development, has emerged as a leading framework in the realm of project management. Its ability to navigate complexities and deliver value incrementally has made it a favored choice for diverse industries seeking efficient and flexible approaches to manage projects. As organizations continue to evolve and embrace agility, Scrum remains a valuable tool in their quest for innovation and success.
Comments
Post a Comment